

With the advancement of technology in recent years, the demand for high-precision optical components has gradually increased. High-quality optical components are essential in semiconductor manufacturing, optical communications, laser systems, and precision measurement instruments.
The production process of optical lenses encompasses several stages, including cutting, grinding, polishing, cleaning, coating, and inspection. Of these, polishing plays a crucial role in determining the surface quality of the lens, which directly impacts production costs.

- Cutting: Rough cutting shapes the optical lens to a certain form, dimensional accuracy, and surface roughness, serving as the initial shaping step.
- Rough Grinding: This step includes rough and fine grinding processes to fix the radius (R value) of the optical lens.
- Fine Grinding: Edge grinding is employed to reduce the outer diameter of the optical lens to the specified dimensions.
- Polishing: The polishing process removes the damaged layer left from fine grinding, achieving the desired surface grade. It also refines the surface profile to meet design specifications, resulting in a smooth and transparent finish. Finally, the lens undergoes wiping and cleaning procedures.
The polishing process is a critical step affecting the precision of optical lenses and is the most important procedure in the optical lens manufacturing process. During polishing, the optical lens is placed on a polishing tool, and polishing liquid (prepared from polishing powder) is introduced to the contact surface of the tool and lens. As the polishing tool or optical lens rotates, relative movement occurs at the contact surface, grinding the surface. Therefore, the performance of the polishing liquid is crucial for the polishing quality of the optical lens. Traditional polishing liquids contain relatively coarse polishing powder particles, typically between 0.5 and 1 μm. Due to the larger particle size, achieving the desired smoothness during polishing with traditional liquids is challenging.
To address these technical issues, DayOptics has designed a polishing method and device for ultra-smooth polishing of optical lenses.
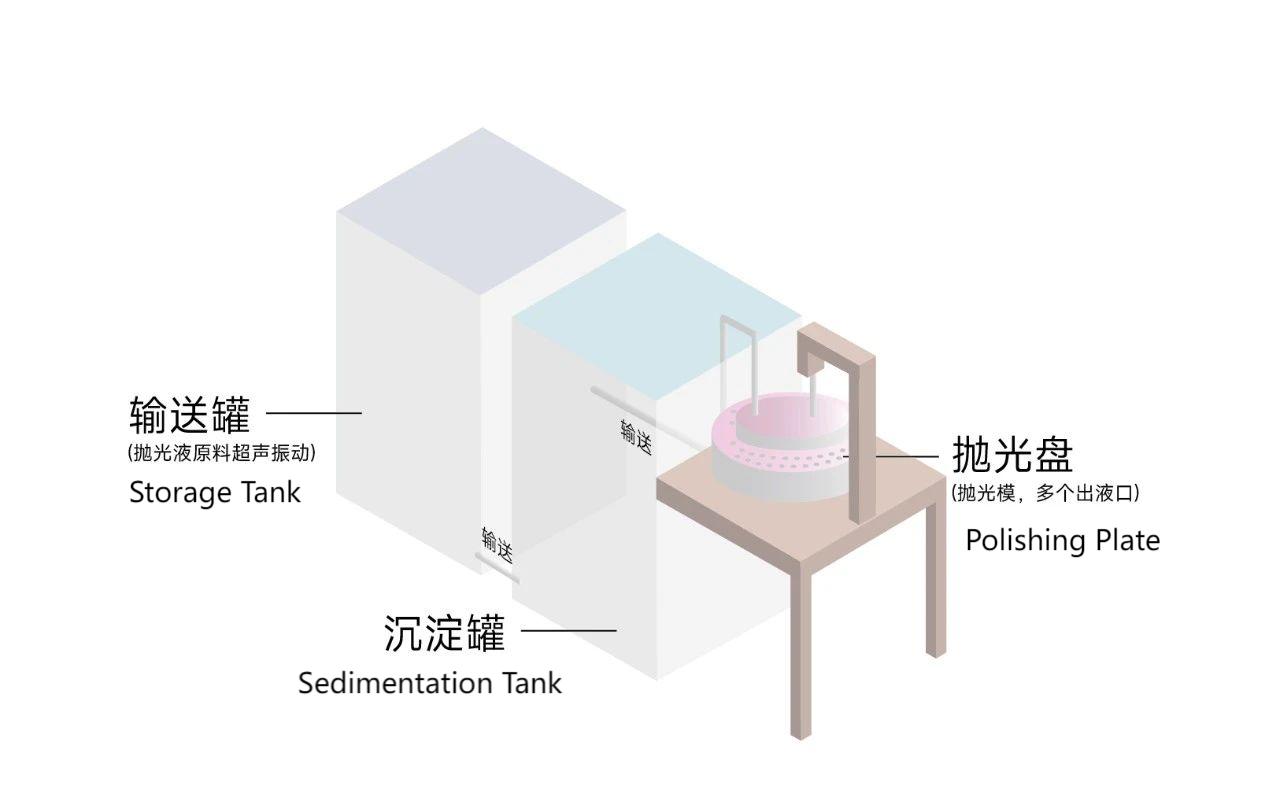
The ultra-smooth polishing device includes:
1. A storage tank for polishing liquid that has undergone ultrasonic vibration.
2. A sedimentation tank.
3. A polishing plate.
The storage tank is equipped with a conveying component; the polishing plate features a polishing mold for the lens, a driving component to rotate the polishing mold, and a fixture to secure the optical lens. The polishing mold is equipped with multiple liquid outlets, and the sedimentation tank has a conveying component to supply the upper liquid from the tank to the multiple outlets. The cooperation of these components allows for the reprocessing of the polishing liquid, significantly reducing the particle size of the polishing powder in the final product. This enables the polished optical lens to meet the required roughness standards.
Polishing Liquid Preparation
The polishing powder and pure water are mixed in a specific ratio to create the polishing liquid raw material. This mixture is subjected to ultrasonic vibration before being stored in a tank. A conveying component transports the polishing liquid from the storage tank to a sedimentation tank for settling, where the upper liquid is taken as the final polishing liquid product. In the preparation step, the mixing ratio of polishing powder to pure water ranges from 1, with N varying between 30 and 70.
After ultrasonic vibration, lubricating oil is added to the polishing liquid raw material, followed by another round of ultrasonic vibration. The polishing liquid raw material, treated with ultrasonic vibration twice, is then stored in the storage tank.
The future of the ultra-smooth polishing process is filled with opportunities and challenges. With ongoing technological advancements and the application of new materials, this process will play an increasingly important role in various fields, including semiconductors, aerospace, and biomedicine. Additionally, the development of automated and intelligent polishing technologies will further drive its application and widespread use.
This process, titled “A Polishing Method and Device for Ultra-Smooth Polishing of Optical Lenses,” is protected by patent, with the patent number: ZL 202311642368.3.